The massive valuations and funding rounds of 2021 left some room for optimism around the state of the Israeli cybersecurity industry in 2022, instilling a sense of security in Q1 of the new year. While other sectors began to feel the shifting tides of the market as the year progressed, capital continued to freely flow into cybersecurity, further reinforcing the belief that it is a persistently resilient outlier in tech, immune to market instabilities and unable to be shocked into a downturn.
After closing the book on 2022 this week, it is safe to say that this optimism was somewhat misguided. With hindsight, 2021 can be categorized as an anomaly that sent the industry into a tailspin, with bloated valuations exceeding actual revenue and funding rounds scaling at what many warned was an unhealthy pace. The repercussions of this spiral are evident in our 2022 analysis of funding and M&A data for the Israeli cybersecurity ecosystem.
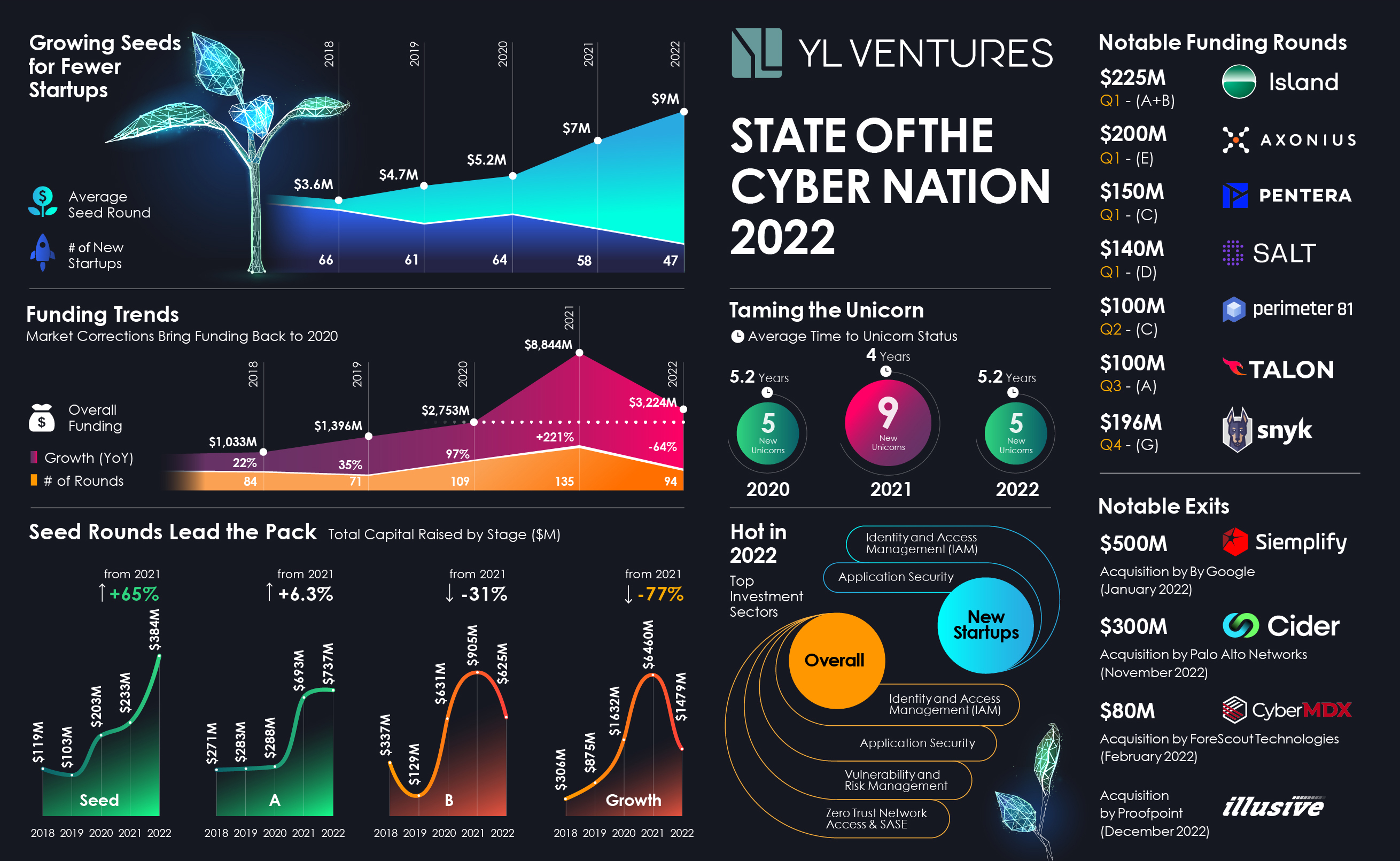
Image Credits: YL Ventures (opens in a new window)
In 2022, overall funding for Israeli cybersecurity startups fell by a dramatic 64%, from $8.84 billion in 2021 to $3.22 billion this year, and the number of funding rounds decreased from 135 in 2021 to 94. When compared to overall funding in 2020 ($2.75 billion over 109 funding rounds), it seems that 2021 was a blip on the radar, and that the industry is returning to where it left off in 2020.
The majority of capital that did flow into Israel’s cybersecurity industry poured directly into seed rounds of early-stage startups.
Early stage gets the funding
Our data indicate that the majority of capital that did flow into cybersecurity this year poured directly into one very distinct area: seed rounds of early-stage cybersecurity startups. The average 2022 seed round actually shattered the 2021 record ($7 million), reaching a whopping $9 million. In total, seed funding rose by 65% this year, from $233 million in 2021 to $384 million in 2022.
This striking amount of capital, dedicated to the earliest stages of company building, demonstrates ongoing investor confidence in the cybersecurity industry’s potential to innovate and build solutions for increasingly acute threats.
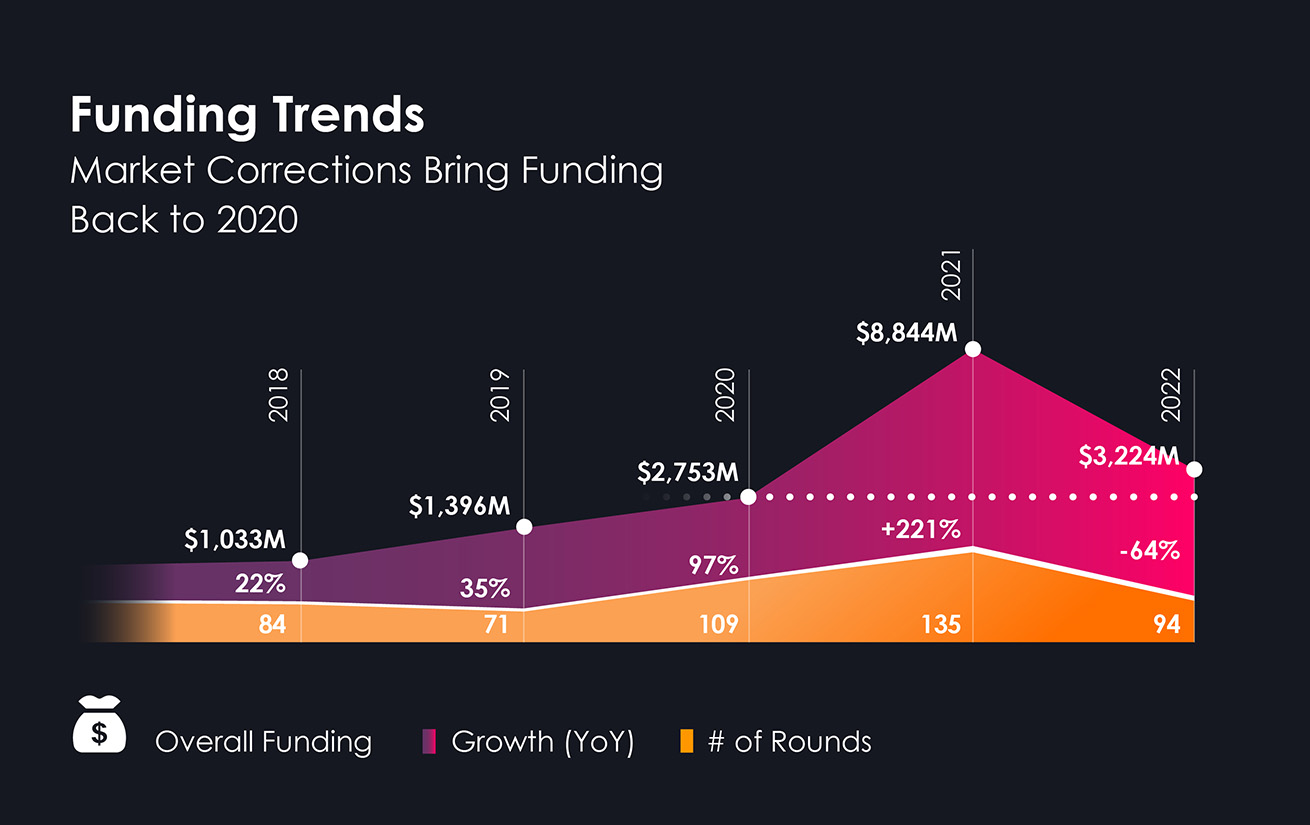
Image Credits: YL Ventures (opens in a new window)
Furthermore, it indicates the difficulty in raising Series A rounds this year, as investors’ thresholds for these rounds grew in light of the economic crisis. While the number of Series A rounds remained almost unchanged since 2021 (30 rounds last year and 24 rounds in 2022), investors preferred to support the seed rounds of startups that will grow sustainably and cautiously from the get-go.
Image Credits: YL Ventures (opens in a new window)
“Investors understand that seed funding has a clear baseline, as the costs of building a company have not decreased,” says Iren Reznikov, director of Corporate Development and Ventures at Sentinel One. “They know that building a company from the ground up and ensuring that it reaches its Series A round with maximum maturity while hitting all of its benchmarks, costs money. At the same time, investors expect founding teams to set clear goals for reaching their Series A and strive to reach product-market fit at an early stage by engaging with prospective customers faster.”
This confidence is shared by cybersecurity founders, who, despite this year’s market volatility, still believe in the potential to build something meaningful for enterprise protection and business continuity. “Early-stage startups are best poised to respond to the changing needs of a fiscally constrained market,” says Slavik Markovich, co-founder and CEO of Descope, a stealth startup building a service for application developers in the authentication space.
“A tight economy is usually accompanied by increased fraud and cyber attacks. User adoption and conversion have become even more critical in this market, with businesses looking for solutions that reduce friction for their end customers in order to prevent any sources of churn. Founding teams at early-stage companies that focus on solving these problems will continue to attract investor interest.”
