OpenAI’s viral AI-powered chatbot, ChatGPT, can now browse the internet — in certain cases.
OpenAI today launched plugins for ChatGPT, which extend the bot’s functionality by granting it access to third-party knowledge sources and databases, including the worldwide web. Available in alpha to ChatGPT users and developers on the waitlist, OpenAI says that it’ll initially prioritize a small number of developers and subscribers to its premium ChatGPT Plus plan before rolling out larger-scale and API access.
Easily the most intriguing plugin is OpenAI’s first-party web-browsing plugin, which allows ChatGPT to draw data from around the web to answer the various questions posed to it. (Previously, ChatGPT’s knowledge was limited to dates, events and people prior to around September 2021.) The plugin retrieves content from the web using the Bing search API and shows any websites it visited in crafting an answer, citing its sources in ChatGPT’s responses.
A chatbot with web access is a risky prospect, as OpenAI’s own research has found. An experimental system built in 2021 by the AI startup, called WebGPT, sometimes quoted from unreliable sources and was incentivized to cherry-pick data from sites it expected users would find convincing — even if those sources weren’t objectively the strongest. Meta’s since-disbanded BlenderBot 3.0 had access to the web, too, and quickly went off the rails, delving into conspiracy theories and offensive content when prompted with certain text.
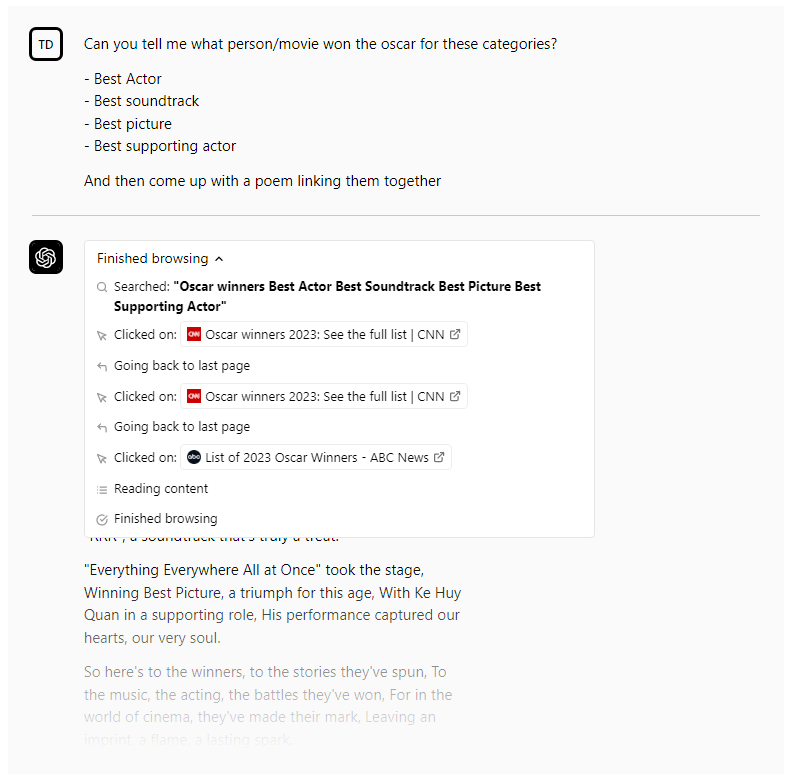
Image Credits: OpenAI
The live web is less curated than a static training data set and — by implication — less filtered, of course. Search engines like Google and Bing use their own safety mechanisms to reduce the chances unreliable content rises to the top of results, but these results can be gamed. They also aren’t necessarily representative of the totality of the web. As a piece in The New Yorker notes, Google’s algorithm prioritizes websites that use modern web technologies like encryption, mobile support, and schema markup. Many websites with otherwise quality content get lost in the shuffle as a result.
This gives search engines a lot of power over the data that might inform web-connected language models’ answers. Google has been found to prioritize its own services in Search by, for example, answering a travel query with data from Google Places instead of a richer, more social source like TripAdvisor. At the same time, the algorithmic approach to search opens the door to bad actors. In 2020, Pinterest leveraged a quirk of Google’s image search algorithm to surface more of its content in Google Image searches, according to The New Yorker.
OpenAI admits that a web-enabled ChatGPT might perform all types of undesirable behaviors, like sending fraudulent and spam emails, bypassing safety restrictions and generally “increasing the capabilities of bad actors who would defraud, mislead or abuse others.” But it also says that it’s “implemented several safeguards” informed by internal and external red teams to prevent this. Time will tell whether those are sufficient.
Beyond the web plugin, OpenAI released a code interpreter for ChatGPT provides the chatbot with a working Python interpreter in a sandboxed, firewalled execution environment along with disk space. It supports uploading files to the current conversation workspace and downloading the results of your work; OpenAI says it’s particularly useful for solving mathematical problems, doing data analysis and visualization and converting files between formats.
A host of early partners built plugins for ChatGPT to join OpenAI’s own, including Expedia, FiscalNote, Instacart, KAYAK, Klarna, Milo, OpenTable, Shopify, Slack, Speak, Wolfram and Zapier. To foster the creation of new ones, OpenAI has open-sourced a “retrieval” plugin that enables ChatGPT to access snippets of documents from data sources such as files, notes, emails or public documentation by asking questions in natural language.
